The Best Time to Plant Grass
When your sights are set on a thick, lush lawn, planting grass seed represents an investment of time, money, labor and hope. From seeding new lawns to repairing rough spots and renewing existing turf, proper timing separates sweet success from something less. Your best time for planting grass seed depends on the type of lawn grass you grow and where you live. Understanding your options and getting timing right helps you seize every opportunity for seeding success.
WHY TIMING MATTERS
Grass grows fastest and strongest when your planting season aligns with the seeds' natural periods of active growth. Just as with other kinds of plants in your landscape, lawn grasses vary in their growth cycles and regional climate preferences.
Cool-season grasses such as Kentucky bluegrass, perennial ryegrass and tall fescue, including Kentucky 31 tall fescue, grow most vigorously during the cool temperatures of late summer and early fall. These grasses flourish across cooler northern climates and into the challenging "transition zone" where cool and warm regions overlap.
Warm-season grasses, such as Bermudagrass, Bahiagrass, Zoysia grass and Centipede grass peak in growth during the warmer temperatures of late spring and early summer. These grasses thrive in southern and western regions and up into the transition zone's southern reaches.
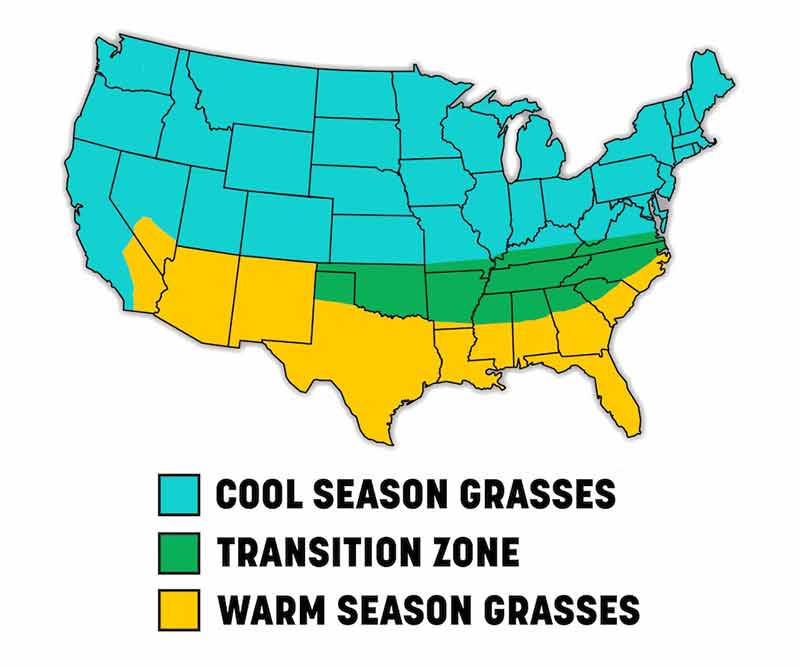
Whether you grow cool- or warm-season grasses, timing your seeding to take advantage of your grass type's natural periods of peak growth helps seed germinate and establish quickly. Your seed gets off to the best possible start and gets on track for both short- and long-term success.
WHY FALL IS BEST FOR COOL-SEASON GRASSES
Several distinct advantages make fall the best time to plant cool-season grass seed. In early autumn, the soil is still warm from months of summer sun. This combination of warm soil, moderate daytime temperatures and cool evenings encourages fast germination and establishment of newly sown cool-season grass seed.
Cool-season grass seed germinates best when soil temperatures reach 50 to 60 degrees Fahrenheit. This roughly corresponds to daytime air temperatures in the 60°F to 75°F range. An inexpensive soil thermometer, available at garden stores and online retailers, can help eliminate the guesswork.
The farther north you live, the earlier cool fall temperatures and ideal planting times come. For example, Minnesotans in the Upper Midwest seed cool-season lawns from mid-August to mid-September.1 For transition-zone lawn owners in central and northern Arkansas, September and October are the best time for seeding cool-season lawns.2
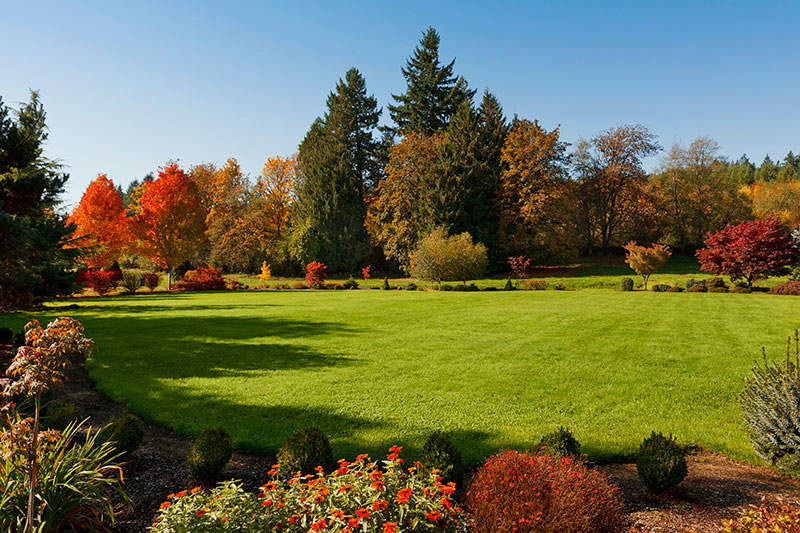

Fall seeding complements the natural growth cycles of cool-season grasses.
As a general rule, plant cool-season grass seed at least 45 days before the estimated date of your first fall frost, before soil and air temperatures drop to less favorable levels. Your grasses will enjoy a full fall season, plus a second cool growing season come spring. Your local county extension agent can help with advice on average frost dates and optimal timing for seeding lawns in your area.
Newly planted seed needs consistent soil moisture, and fall planting offers benefits on that front, too. Fall typically brings more precipitation, which lessens the chance that cool-season seeds may dry out, and reduces the need for extra watering on your part. Using premium drought-tolerant, water-conserving grass seed products, such as Pennington Smart Seed and Pennington Smart Patch II mixes, lowers the risk of problems even more.
The second best time to seed cool-season lawn grasses is in the spring, once soil and air temperatures warm back up to their optimal range. However, late-melting snows and early spring rains can keep soil cold and overly wet, giving early weeds an advantage. Grasses also have less time to settle in before higher temperatures inhibit germination and cool-season grass growth begins to slow.
WHY SPRING IS BEST FOR WARM-SEASON GRASSES
Warm-season grasses germinate best when soil temperatures are consistently in the 65°F to 70°F range. This generally corresponds to daytime air temperatures near 80°F or more. Planting in late spring and early summer gives warm-season grasses the advantage of warm soil and early seasonal rains, which help keep soil moisture available during germination and establishment.
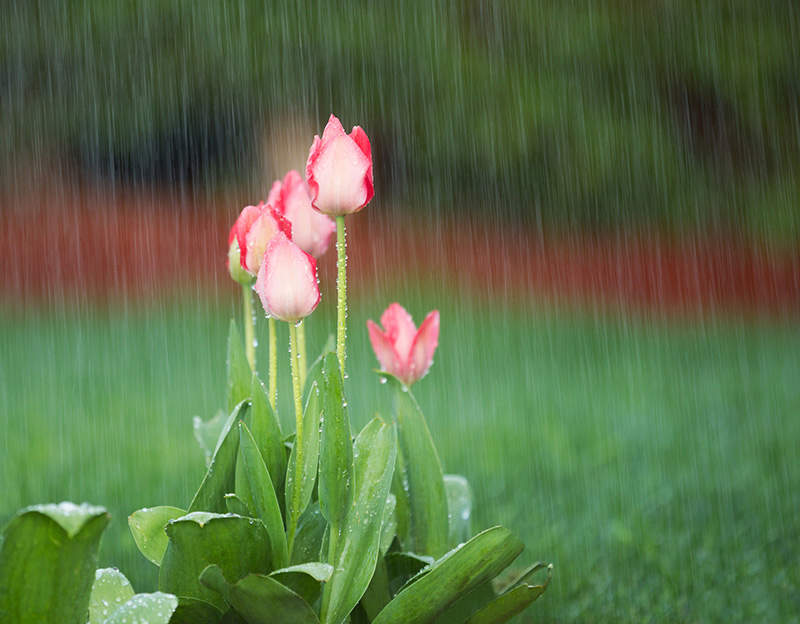

As with cool-season grasses, best warm-season planting times vary by location. In California, mid-April to mid-May is prime time for seeding warm-season lawns.3 In central and southern Arkansas, lawn owners plan their warm-season grass seeding for late May through June.2 It's tempting to get out and seed at the first hint of spring, but patience pays off. Wait until all danger of frost has passed and soil warms. Cold, wet soil is a recipe for poor germination, rotting seed and disease. Your county extension agent can help with expected frost dates and timely advice when unexpected weather conditions factor in.
As a general rule, warm-season grasses planted at least 90 days before the first fall frost have time to establish well before winter. These summer-loving grasses go dormant once temperatures drop near 55°F, so late-planted seedlings can't prepare for what's ahead. With proper timing, warm-season grass seed gets a natural boost from summer's warmth and a full season of active growth and development before cooling temperatures bring on winter dormancy.
One exception to the spring seeding rule for warm-season lawns is when overseeding with a cool-season grass, such as perennial ryegrass, for temporary winter color. Overseeding for green winter grass is always done in fall, once temperatures drop and warm-season lawns begin to go dormant and lose color.


WHAT TO EXPECT FROM NEWLY PLANTED GRASS SEED
Proper timing allows all types of grass seedlings to root well and get established before natural stresses hit. What that looks like in your lawn can vary depending on your grass type, your growing region and the conditions in any given year.
Grass types and varieties vary in their natural germination speeds. For example, cool-season Kentucky bluegrass germination can take two to three times as long as tall fescue varieties. Similarly, warm-season Zoysia grass may take two to three times longer than Bermudagrass. In addition, many seed products include a mix of seed types that germinate at different speeds.
Whether you're repairing bare spots, overseeding an existing lawn or starting from scratch, you can generally expect grass seedlings to emerge within seven to 21 days when grown under proper conditions. It may take another three to four weeks of growth before grass is long enough to mow. For fall-planted seed, this can mean waiting until spring for your first mowing. Some grasses, such as Zoysia grass, may need several months of growth to fully establish.
Much of the initial growth of new grass seedlings happens underground, where you can't see it. New roots get grass firmly established, prepared for the seasons ahead and positioned for strong, rapid growth when their peak season arrives. With proper timing, new grass seedlings compete well for light, water and nutrients and fight off lawn diseases and pests, including lawn weeds.

HOW TO MAXIMIZE THE TIMING ADVANTAGE
Even when you plant your grass seed at the best possible time, your lawn still needs help to thrive. Whether this is your first lawn or you're the neighborhood expert, take some advice from turf professionals and get to know your grasses and your soil before you start seeding. Follow through on best practices for preparing and planting and don't neglect traditional tasks, such as fall lawn care, that help keep your grass and soil healthy, well-nourished and ready to support new growth.
Do your research to understand what's in a bag of grass seed and the company behind the seed. Pennington is committed to producing the finest grass seed products possible and providing you with educational resources to help your seed project succeed. By timing your lawn tasks properly, you can maximize your advantage and seed your way to the lawn of your dreams.
Pennington, Smart Seed and One Step Complete are trademarks of Pennington Seed, Inc.
Sources:
1. Mugaas, R. and Pedersen, B., "Seeding and Sodding Home Lawns," University of Minnesota Extension.
2. Patton, A. and Boyd, J., "Seeding a Lawn in Arkansas," University of Arkansas Cooperative Extension Service.
3. UC Statewide Integrated Pest Management Program, "Planting Times and Rates for Grasses That Can Be Established From Seed," University of California.




